Displaying items by tag: DNA preservation
Grape Archaeology and Ancient DNA Sequencing
 Guasch-Jané M.R. (2019) Grape Archaeology and Ancient DNA Sequencing. In: Cantu D., Walker M. (eds) The Grape Genome. Compendium of Plant Genomes. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-18601-2_4
Guasch-Jané M.R. (2019) Grape Archaeology and Ancient DNA Sequencing. In: Cantu D., Walker M. (eds) The Grape Genome. Compendium of Plant Genomes. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-18601-2_4
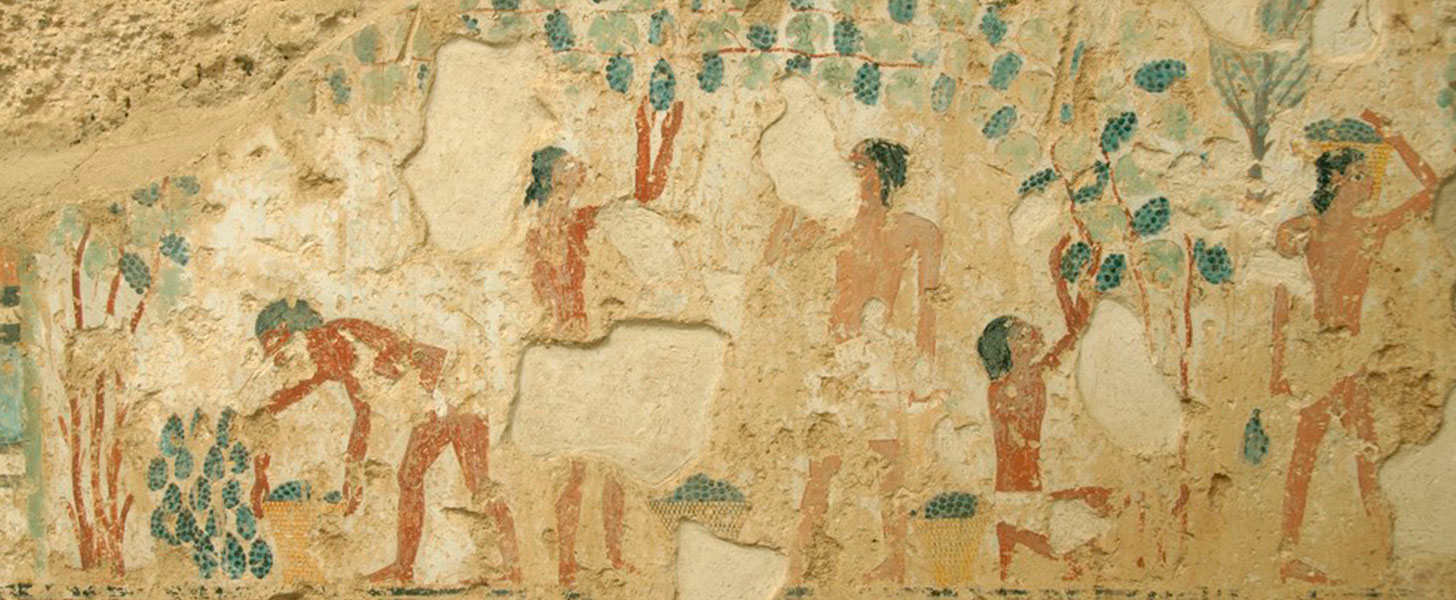
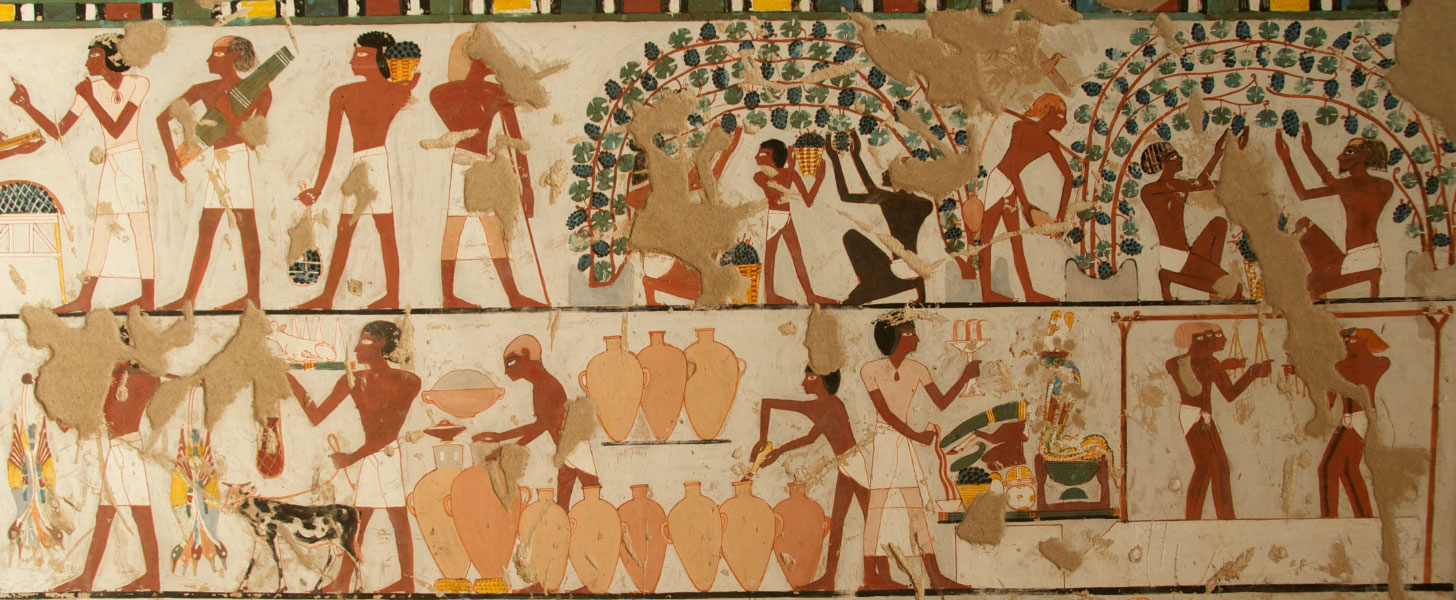
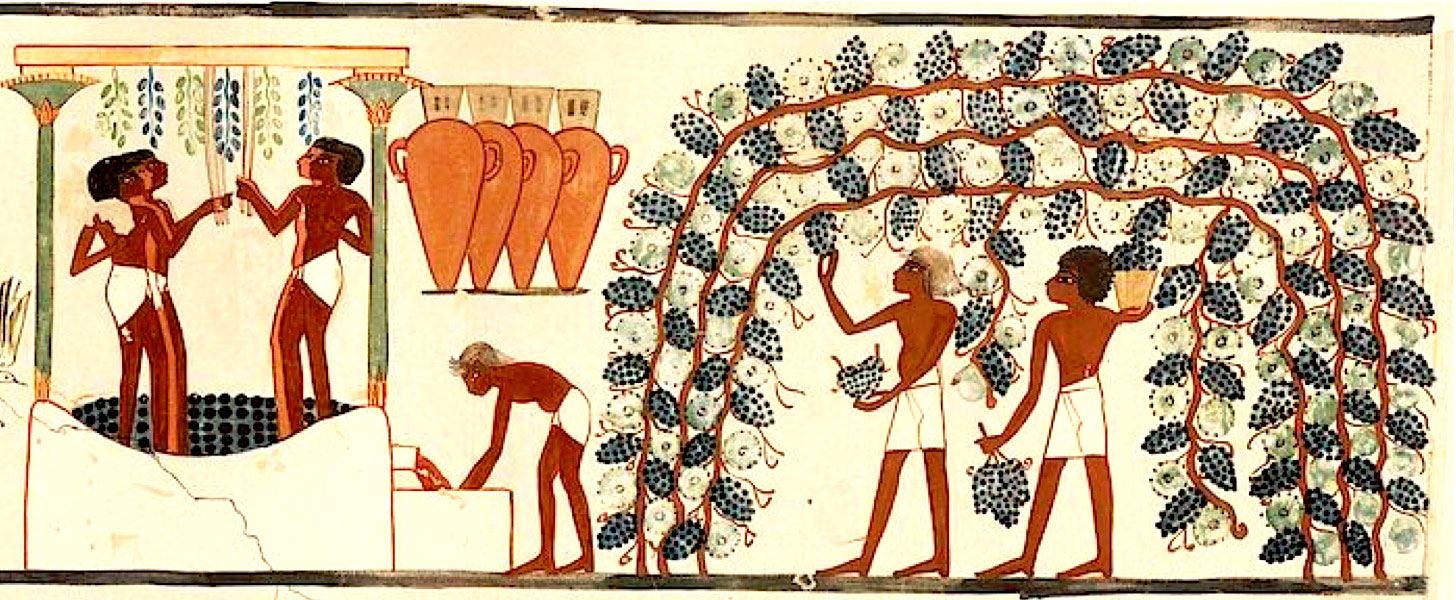
Abstract The cultivation and domestication of the grape appears to have occurred between 7000 and 4000 BC. The archaeological and historical evidences suggest that the domestication of the grapevine took place in the Near East. Nevertheless, whether a single origin or secondary independent grapevine domestications occurred and where they happened remains so far unanswered. Wine has had an important role in religious rituals since Antiquity. In mythology and theology, wine was symbolic of the power to revitalize and rebirth. In Ancient Egypt, wine was daily served to the gods by the Pharaoh and the priests in ritual ceremonies in the Egyptian temples. In daily life, wine was an enjoyable drink consumed by the elite in festivals, banquets and funerals. Further, the grape was one of the most important fruits in the Classical Mediterranean civilizations and grapevines and the wine were widely spread through trade sea routes. This chapter presents an overview of the archaeological evidence for wine culture in the ancient Near East, Egypt and the Mediterranean region. It also presents a discussion of the chemical and morphological research methods and paleogenomic analyses and discussion that have been applied to ancient grape and plant material.
Keywords: Ancient DNA, Amphora, DNA preservation, Grape domestication, Wine archaeology.
DOI https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-18601-2_4
Print ISBN978-3-030-18600-5
Online ISBN978-3-030-18601-2